18 September, 2023
Hello and welcome to this week’s JMP Report
Last week saw 6 stocks trade on the local market. BSP traded 1,879 shares, closing 7t higher at K13.27. KSL traded 143,191 shares closing 1t higher at K2.42. STO traded 5,791, closing 10t higher at K19.21. KAM traded 22,392, closing 5t at K0.95. CCP traded 9,000 shares, closing 5t lower at K2.00 and CPL traded 48,530 shares, closing steady at K0.79.
WEEKLY MARKET REPORT | 11 September, 2023 – 15 September, 2023
| STOCK | QUANTITY | CLOSING PRICE | CHANGE | % CHANGE | 2022 FINAL DIV | 2023 INTERIM | YIELD % | EX-DATE | RECORD DATE | PAYMENT DATE | DRP | MARKET CAP |
| BSP | 1,879 | 13.27 | 0.07 | 0.53 | K1.4000 | K0.370 | 13.33 | FRI 22 SEPT 2023 | MON 25 SEPT 2023 | FRI 13 OCT 2023 | NO | 5,317,971,001 |
| KSL | 143,191 | 2.42 | 0.01 | 0.41 | K0.1610 | K0.097 | 10.75 | WED 6 SEPT 2023 | THU 7 SEPT 2023 | THU 5 OCT 2023 | NO | 64,817,259 |
| STO | 5,791 | 19.21 | 0.1 | 0.52 | K0.5310 | K0.314 | 4.42 | MON 28 AUG 2023 | TUE 29 AUG 2023 | THU 28 SEPT 2023 | – | – |
| KAM | 22,392 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 5.26 | – | K0.12 | 12.63 | TUE 19 SEP 2023 | WED 20 SEP 2023 | THU 19 SEP 2023 | YES | 49,891,306 |
| NCM | 0 | 75.00 | – | 0.00 | USD$1.23 | K0.719 | 2.60 | FRI 18 AUG 2023 | MON 21 AUG 2023 | MON 18 SEPT 2023 | – | 33,774,150 |
| NGP | 0 | 0.69 | – | 0.00 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 32,123,490 |
| CCP | 9,000 | 2.00 | -0.05 | -2.50 | K0.123 | – | 6.15 | FRI 24 MAR 2023 | WED 29 MAR 2023 | FRI 5 MAY 2023 | YES | 569,672,964 |
| CPL | 48,530 | 0.79 | – | 0.00 | K0.02 | – |
2.50 |
WED 22 MAR 2023 | THU 30 MAR 2023 | THU 30 JUL 2023 | – | 195,964,015 |
Dual Listed Stock PNGX/ASX
BFL – 5.36 +10c
KSL – 0.795 +3c
NCM – 26.09 +37c
STO – 7.91 +13c
Our Order Book
We are nett buyers of STO, BSP, CCP, KSL
Interest Rates
On the interest rate front, we are seeing some upward pressure coming into the short end. The Bank came to the market with only 7day stock, with 2.04bill on offer which was filled by the market at an average of @ 2%. The 364 day TBills rose to 3.02% with 88mill oversubscribed.
We did see a GIS auction announcement last week with 8maturities on offer out to 5/2033. Auction date is September 19 and we will bring you the results in next weeks report.
Other Assets we track
Silver – 23.32 +12c
Natural Gas – 2.63 +4c
Bitcoin – 26,529 +2.73%
Ethereum 1,623 +0.38%
PAX Gold – 1,910 +0.68%
What we’ve been reading this week
Uranium Price Guide: Trends, Factors, and Future Predictions
Carbon Credits

With its importance in the global energy landscape, the uranium price has become a hot topic for investors, policymakers, and energy enthusiasts. The world is evolving, and as technology advances, the need for efficient energy sources becomes paramount.
Among the plethora of energy resources, uranium stands out as a vital ingredient in nuclear power generation. Understanding the dynamics, factors affecting its prices, and potential future trends is essential for anyone keen on the energy sector.
Historical Trends in the Uranium Price
The history of uranium prices can be characterized as a roller-coaster ride. In the early days of nuclear energy, during the mid-20th century, there was an initial surge in demand. Prices peaked in the late 1970s, driven by energy crises and a burgeoning interest in nuclear power as a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels.
However, major incidents like the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 and the Fukushima Daiichi disaster in 2011, affected public perception of nuclear energy and its safety, causing significant dips in demand and consequently, prices.
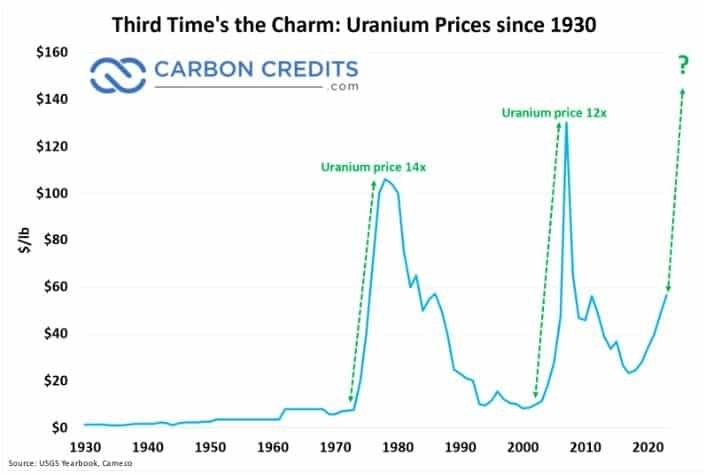
But, as safety protocols improved and with the global push for cleaner energy, the value of uranium has seen a steady increase here in 2023.
Historic Uranium Price Spikes
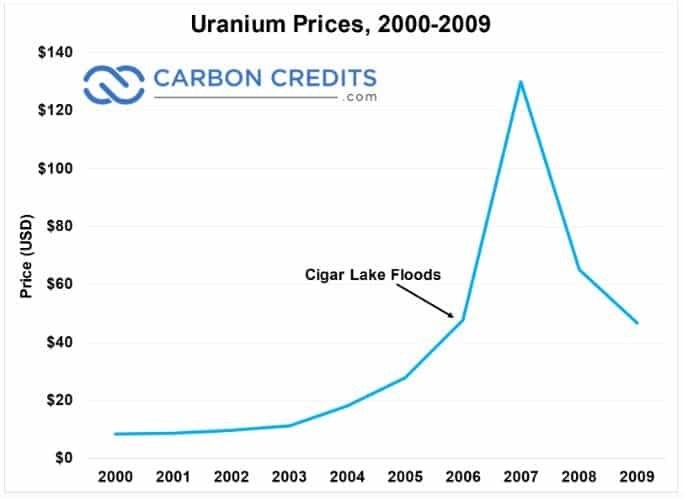
Cigar Lake holds the largest reserve of high-grade uranium—at 100x average grade—anywhere in the world. And at the time it was supposed to be completed, it would have produced more than 10% of the world’s supply.
But when a small standpipe in Shaft No. 2 sprang a leak, two workers trying to fix it accidentally broke a valve completely off.
The gush of water couldn’t be stopped, and the mine flooded—several times. Mine development couldn’t resume for four years. The mere possibility of a tighter supply, combined with planned nuclear construction around the world, sent shockwaves through the entire uranium market.
The uranium price spiked from $20/lb. to $140/lb. in early 2007.
Cameco, the company that owns Cigar Lake, couldn’t have been happier with the payout. Despite its largest project—by far—having just been delayed by nearly a decade, Cameco’s stock rose by 300 percent from 2005–2007.
But ultra-high uranium prices led to historically high exploration and production… and the price began to return to normal. Then Fukushima happened in 2011, and it was Three Mile Island all over again.
As a result, the price fell to one of the lowest inflation-adjusted levels in history. And it stayed there.
Factors Influencing Uranium Prices
Several key elements play a role in determining the uranium price:
- Supply and Demand:Like any other commodity, uranium prices are heavily influenced by supply and demand dynamics. As more countries adopt nuclear power and existing nuclear plants expand, the demand for uranium increases. Meanwhile, supply constraints can arise from mining challenges, geopolitical issues, or strategic stockpiling.
- Production Costs:Mining uranium is capital intensive. The cost of production, influenced by factors like ore quality and extraction methods, has a direct bearing on its price. When the production cost is high, it can set a floor for uranium prices, as miners wouldn’t sell below their cost of production.
- Regulations and Policies:National and international regulations can sway uranium markets. Stringent safety and environmental guidelines can increase production costs, whereas supportive policies, such as those promoting clean energy, can boost demand.
- Alternative Energy Sources:The rise of renewables like solar and wind energy can influence uranium demand. While nuclear energy offers consistent power generation unlike some renewables, the growth of alternative energy sources can impact uranium’s market dynamics.
Uranium Price Future Outlook
Looking forward, several factors may influence the uranium price. One of the most significant is the role of nuclear energy in the global quest to combat climate change. This includes major corporate initiatives as well as government policy to reduce emissions.
As nations strive to reduce carbon emissions, nuclear power, despite its critics, presents a viable option for a consistent and large-scale energy source.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia, are investing heavily in nuclear power. Countries like China and India, with their burgeoning populations and increasing energy needs, are looking towards nuclear energy to supplement their energy grids. This, in turn, will lead to a steady increase in demand for uranium in the coming years.
How High Can Uranium Prices Go?
According to Katusa Research, a distinct characteristic of the uranium market is its near-inelastic demand. Utility companies are compelled to purchase uranium for their reactors, irrespective of the uranium price.
- Even if uranium’s price shifts from $45 to $450 per pound, the change in cost per kilowatt-hour is minimal, especially when compared to equivalent price surges in natural gas or coal.
- To illustrate, if there’s a tenfold price hike in uranium, the cost for electricity generation from a nuclear reactor would only rise by about 24%.
Additionally, innovations in nuclear technology, including small modular reactors and next-generation reactors, might not only increase the efficiency of uranium usage but also boost its demand.
Uranium and the Acceleration of Nuclear Energy
The uranium price is more than just a number; it’s an indicator of the global energy landscape.
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and energy security, uranium will likely continue to play a significant role in the global energy mix.
- 440 nuclear power plants operating in 33 countries combined to provide 10% of the world’s electricity
- Globally, a total of 90 nuclear reactors are on order or planned, with over 300 more in the proposal stage.
- Nuclear energywill play a major role in the global energy mix as the world moves towards net zero emissions
The International Energy Agency says that the nuclear industry will need to double in size over the next two decades for us to meet net zero emissions targets.There are just over 400 nuclear reactors in operation around the world right now.
Future Uranium Price Dynamics: No Net Zero Without Nuclear
Far from reducing emissions—or even keeping them the same—for every reactor that is forced to shut down, CO2 emissions rise by 5.8 MT a year. That’s the equivalent of filling an NFL stadium to the brim with gas, and setting it on fire.
We’d need to install solar panels on one million homes just to make up for shuttering a single reactor. Nuclear reactors are extremely efficient, low-carbon sources of energy. In fact, it doesn’t matter whether it’s replacing coal or natural gas:
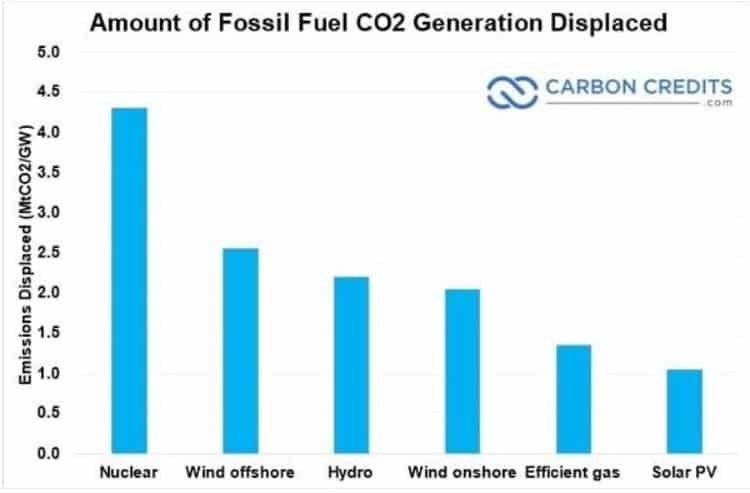
- Nuclear is nearly 100 percent more effective than any other energy technology at reducing CO2 emissions.
There is simply no achieving net zero without nuclear. Staying informed about its price trends and underlying factors can offer insights not just into the nuclear energy sector, but the broader trajectory of our global energy future.
EU Commission Considers Requiring Sustainability-Related Disclosures for All Financial Products
Mark Segal

The EU Commission on Thursday announced the launch of a consultation on its sustainable financial disclosure practices, including questions asking for feedback on introducing sustainability-related disclosure requirements for all financial products offered in the EU, even if those products have not made any sustainability claims.
The Commission’s consultation is focused on the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR), which sets out how financial market participants, such as asset managers, have to communicate sustainability information to investors, regarding the integration of sustainability risks and the consideration of adverse sustainability impacts in their processes and the provision of sustainability‐related information with respect to financial products.
The regulation includes classification levels for sustainability-focused investment funds, each with varying disclosure requirements, including ‘Article 8’ funds that “promote environmental or social characteristics or a combination of those characteristics,” and the more stringent ‘Article 9’ funds, “which have sustainable investment as their objective.”
One of the regulation’s key requirements, and among the most challenging for asset managers, is for reporting on Principal Adverse Impact (PAI) that investment decisions have on a broad range of sustainability factors, such as climate and environment, as well as social and employee matters, respect for human rights, anti-corruption and anti-bribery aspects.
While the consultation explains that the SFDR was designed to require products that make sustainability claims “to disclose information to back up those claims and combat greenwashing,” it notes that these requirements “could be viewed as placing additional burden on products that factor in sustainability considerations,” and asks respondents to consider if all products “regardless of related sustainability claims,” should have uniform disclosure requirements.
The consultation adds that this move could also have the benefit of allowing investors to understand products’ sustainability performance even for products that don’t make sustainability claims.
The consultation continues to ask what disclosure requirements should be considered for all financial products, listing taxonomy-related disclosures, engagement strategies, exclusions, and information about how ESG-related information is used in the investment process.
In addition to the potential disclosure requirement changes, and questions about the current functioning of the SFDR regulations, the EU Commission’s consultation also included questions on developing more “precise EU-level product categorisation system based on precise criteria” for sustainable financial products beyond its current “Article 8 and 9” categories.
Following the launch of the consultation, Mairead McGuinness, Commissioner for Financial Services, Financial Stability and Capital Markets Union, said:
“Sustainability information is key to empowering investors to make informed decisions on their investments. Since the Sustainable Finance Disclosures Regulation (SFDR) was proposed in 2018, a lot has changed in the world of sustainable finance. Today we are launching an in-depth three-month consultation for stakeholders. We want to know if our rules meet their needs and expectations, and if it is fit for purpose.”
Responsible ITAD & E-Waste Recycling is a Fast Track to Achieving ESG and Circular Economy Goals for Any Business

By John Shegerian, Chairman and CEO of ERI
One of the lesser-known strategy for companies to attain their ESG and decarbonization targets is the responsible recycling of electronic waste.
E-waste is the fastest growing solid waste stream on the planet — by a margin of 2 to 4 times the speed of the second fastest growing stream. Spurred by increasing consumer demand for the newest technologies and the shortening life spans of many devices, e-waste is piling up in landfills both domestically and abroad. Despite the steady increase in the amount of e-waste being generated each year, a mere 17% is being responsibly recycled.
The straightforward solution: enterprises and all types should explore the responsible recycling of their e-waste. By realizing the potential of responsible ITAD and e-waste recycling disposal, businesses can make significant strides towards fulfilling their ESG goals and circular economy ambitions.
A Circular Economy
Through the recycling of e-waste, businesses can substantially mitigate their ecological impact and align with the “E” in ESG. E-waste frequently contains hazardous materials and valuable resources, underscoring the importance of appropriate disposal and resource reclamation.
Embracing responsible e-waste recycling can be a significant step towards realizing circular economy goals. Rather than perpetuating the linear “take, make, dispose” model, a circular economy minimizes waste, conserve resources, and promote sustainable product lifecycles. By ensuring that discarded electronic devices are recycled and reintegrated into the production cycle, businesses contribute to a more sustainable and efficient economic model.
Electronic devices are a perfect entry point into the circular economy. To make a tablet or cellphone, you have a metal or plastic case, computer components, wires, etc. Metals such as copper, iron, silver, lead, tin, and aluminum are typically mined from the earth and then used in manufacturing to create components required for new devices.
By working with an e-waste recycling or ITAD company that is transparent and able to track all materials from each device processed, an opportunity is created for businesses to not only do the right thing for the planet, but also demonstrate their impactful efforts via ESG or sustainability reports.
A Distinct Advantage for Businesses
E-waste recycling also offers tangible business advantages. It enhances brand reputation and constituent trust. Consumers today value businesses that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. By responsibly managing e-waste, businesses position themselves as responsible corporate citizens and environmental stewards.
Extracting valuable materials from recycled electronics also reduces the need for purchasing virgin resources, resulting in potential cost efficiencies.
In short, responsible e-waste recycling is a direct stride toward achieving ESG objectives and fostering a circular economy. By harnessing the environmental, social, and business advantages of appropriate e-waste disposal, a company of any size can make significant progress in the effort to reduce its environmental footprint, conserve resources, and enhance its reputation.
Incorporating responsible e-waste recycling into an ESG strategy is an easy win that literally is in the palms of all of our hands.
About the author:
John Shegerian is Chairman and CEO of ERI, the largest fully integrated IT and electronics asset disposition provider and cybersecurity-focused hardware destruction company in the United States. ERI is the first and only company in its industry to achieve carbon neutrality at all its facilities nationwide, and the first to achieve SOC 2 Type I and II certifications for security and data protection. ERI has the capacity to process more than a billion pounds of electronic waste annually at its nine certified locations, serving every zip code in the United States. ERI’s mission is to protect people, the planet and privacy. For more information about e-waste recycling and ERI, call 1-800-ERI-DIRECT or visit https://eridirect.com.
We hope you have enjoyed the read this week. If you would like to discuss your investment alternatives or simply would like to start investing, please feel free to reach out.
Regards,
Head, Fixed Interest and Superannuation
JMP Securities
Level 1, Harbourside West, Stanley Esplanade
Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea
Mobile (PNG):+675 72319913
Mobile (Int): +61 414529814